Publications
Displaying 1 - 10 of 23
The low cost of coal relative to alternative energy sources is slowing progress towards energy transition in many regions
Phasing out coal use requires a reliable and stable alternative energy supply, plus support to the economic and employment transition in regions dependent on coal production
Firms in the United States and Japan are facing capacity constraints
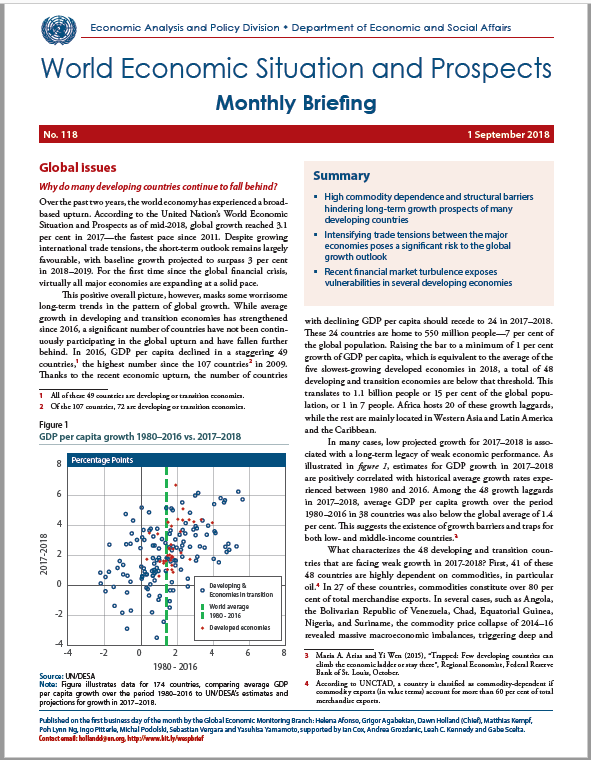
Manufacturing activity slows in developed and developing economies
China turns to pro-growth measures to mitigate the impact of the trade disputes
Fiscal pressures creating significant policy challenges in Latin America
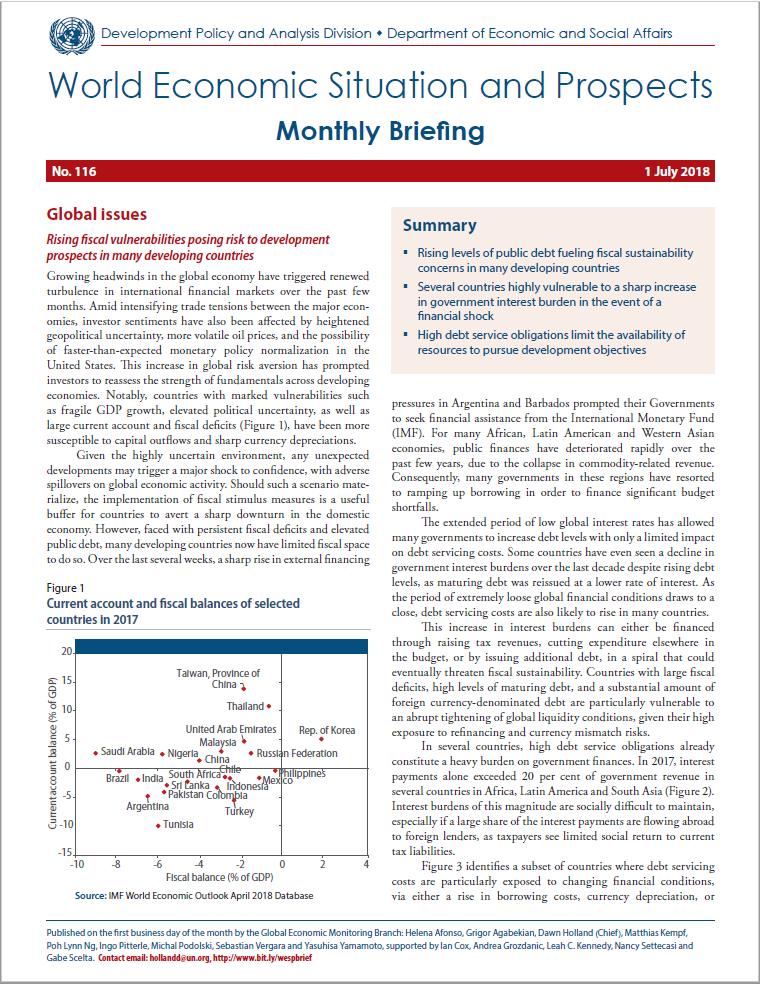
Several countries highly vulnerable to a sharp increase in government interest burden in the event of a financial shock
High debt service obligations limit the availability of resources to pursue development objectives
 Welcome to the United Nations
Welcome to the United Nations