Publications
Displaying 1 - 6 of 6
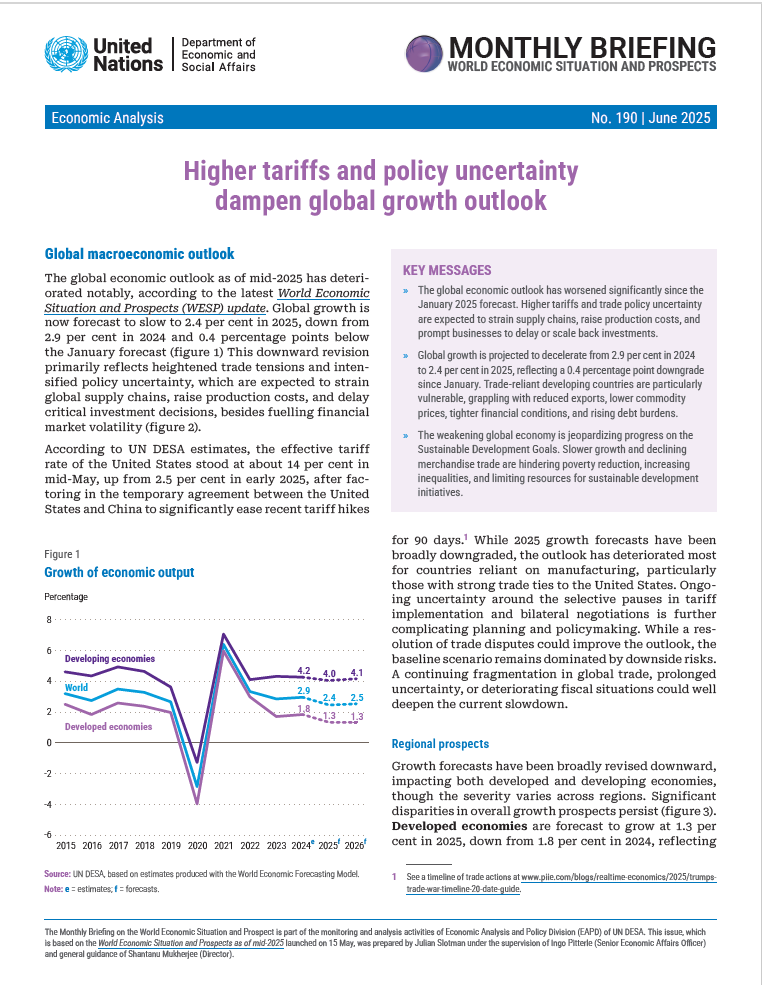
Global macroeconomic outlook The global economic outlook as of mid-2025 has deteriorated notably, according to the latest World Economic Situation and Prospects (WESP) update. Global growth is now forecast to slow to 2.4 per cent in 2025, down from 2.9 per cent in 2024 and 0.4 percentage points below the January forecast (figure 1) This downward revision primarily reflects heightened trade tensions and intensified policy uncertainty, which are expected to strain global supply chains, raise production costs, and delay critical investment decisions, besides fuelling financial market volatility (figure 2). According to UN DESA estimates, the effective tariff rate of the United…
 Welcome to the United Nations
Welcome to the United Nations