Publications
Displaying 11 - 20 of 49
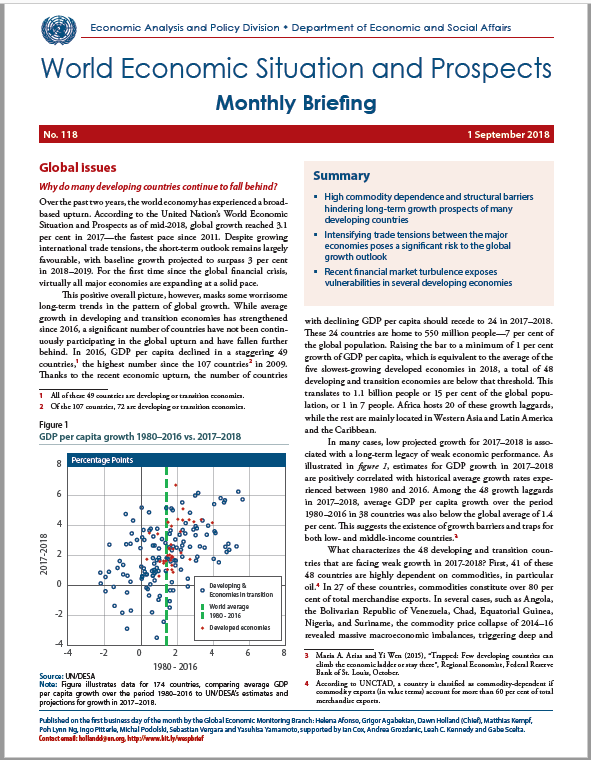
growth outlook Recent financial market turbulence exposes vulnerabilities in several developing economies English: PDF (176 kb) Global issues Why do many developing countries continue to fall behind? Over the past two years, the world economy has experienced a broad-based upturn. According to the United Nation?s World Economic Situation and Prospects as of mid-2018, global growth reached 3.1 per cent in 2017?the fastest pace since 2011. Despite growing international trade… World Economic Situation And Prospects: September 2018 Briefing, No. 118
عربي, 中文, English, Français, Русский, Español
 Welcome to the United Nations
Welcome to the United Nations